Lower back pain significantly decreases life quality by impacting physical and emotional health. This prevalent issue is often exacerbated by sedentary modern workplaces and poor ergonomics. Chronic lower back pain’s complexity necessitates a comprehensive treatment approach addressing both the physical symptoms and emotional distress. Exploring solutions and preventative measures is crucial to tackling this global health concern.
Understanding Lower Back Pain
Lower back pain, a prevalent global health issue, impacts individuals both physically and emotionally, often causing stress, anxiety, depression, and mobility restriction. Modern workspaces can exacerbate this health concern, with improper desk ergonomics leading to strain, poor posture, and pain in the lower back. This ailment is chronic, persistently affecting an individual’s quality of life, demanding a multifaceted understanding. The approach to lower back pain treatment should be comprehensive, considering the chronic nature, emotional toll, and ergonomic factors, enabling effective relief.
Common Causes of Backache
Backache, a common issue, results from lifestyle factors, medical conditions, and injuries. Lifestyle factors include daily habits and routines. Certain medical conditions inherently cause back pain. Injuries, particularly back trauma, often lead to prolonged discomfort.
Lifestyle Factors and Backache
Backache is significantly influenced by lifestyle factors such as lengthy sedentary behavior, poor posture, and inadequate stress management.
- Lengthy Sedentary Behavior: The increase in desk jobs has led to prolonged sitting, straining the lower back. Mitigation requires regular breaks and physical activity.
- Poor Posture: Slouching places extra stress on back muscles. Workspace optimization through ergonomic evaluation fosters improved posture.
- Inadequate Stress Management: High stress levels result in back muscle tension, increasing injury susceptibility. Effective stress management techniques include deep breathing, yoga, and mindfulness.
These factors highlight the necessity of lifestyle alterations for lower back pain relief and prevention.
Medical Conditions Causing Backache
Backache can stem from various medical conditions. Genetic predispositions can lead to backache-related conditions like degenerative disc disease or spinal stenosis. Psychological factors such as stress and anxiety can cause muscular tension, resulting in lower back discomfort. Chronic illnesses, including arthritis, kidney diseases, and infections, can induce backache. Understanding these potential causes is essential for effective back pain management and treatment.
Injuries Leading to Backache
Backache, a common health issue, often stems from physical injuries.
- Musculoskeletal Strains: Resulting from heavy lifting, sudden movements or improper body mechanics, these strains can cause muscle spasms and backache. Recovery hinges on rehabilitation exercises.
- Disc Injuries: Leakage from the spinal disc’s soft center irritates nearby nerves, causing backache. Posture correction can mitigate this pain.
- Spinal Fractures: High-impact trauma or osteoporosis can lead to these painful injuries, necessitating a thorough rehabilitation process.
Recognizing these causes informs backache prevention and treatment strategies.
Symptoms Indicating Lower Back Pain
Recognizing lower back pain symptoms is critical for early treatment. These include discomfort in the lower back, often linked to decreased mobility, impacting daily tasks. Detailed analysis of these symptoms promotes awareness and encourages early action.
Identifying Lower Back Discomfort
Lower back discomfort, a prevalent condition, presents distinct physical and psychological symptoms aiding in its diagnosis.
- Physical Symptoms: A sharp or dull ache characterizes it, intensifying with movement, either constant or intermittent, localized or radiating to buttocks or legs.
- Functional Limitations: Impaired ability to perform routine tasks like bending, lifting, or walking, indicating musculoskeletal issues.
- Psychological Effects: Chronic pain in the lower back may result in increased stress, anxiety, or depression, amplifying pain perception, significant in the diagnosis process.
Link Between Pain and Mobility
Lower back pain often leads to decreased mobility, indicating a strong correlation between discomfort and daily physical activity. Pain Psychology notes that persistent lower back pain can cause emotional stress, potentially worsening the condition. This stress may be due to ongoing discomfort, movement fear, or worry about long-term pain effects. Therefore, assessing a patient’s emotional health is essential to understand their condition fully, providing insights into the pain, mobility, and emotional wellbeing connection.
Impact on Daily Activities
Lower back pain impacts daily activities significantly, necessitating the early identification of symptoms. This pain disrupts regular activities, diminishing life quality.
- Psychological Impact: Pain can induce psychological distress, such as anxiety and depression, hindering enjoyment and social activities participation.
- Sleep Disruption: Lower back pain can disturb sleep, resulting in daytime fatigue and reduced productivity.
- Physical Activity Limitations: Pain can curtail physical activity, complicating routine tasks such as lifting, bending, or walking.
Risk Factors for Developing Back Pain
Genetic predisposition, occupational hazards, and age are key risk factors for back pain. Research indicates a higher likelihood of back pain in individuals with a family history due to inherited characteristics such as disc degeneration, spinal structure, and body weight distribution.
Occupations demanding heavy lifting, bending, twisting, prolonged sitting, standing, or using vibrating machinery increase back strain, thus upping pain risks.
Ageing also elevates back pain risk through decreased muscle elasticity, bone strength, and conditions like osteoporosis, arthritis, and spinal stenosis. Knowledge of these risk factors aids in effective prevention.
Impact of Lifestyle on Back Health
Lifestyle impacts back health significantly. Habits like inactivity, poor diet, and smoking degrade spinal structures, increasing back pain prospects. Modifying these factors enhances back health and reduces chronic pain risk.
- Ergonomic Workspaces: Long-term sitting with incorrect posture strains the spine, causing discomfort and injury. Ergonomic workspaces, including adjustable seating and desks, footrests, and optimal computer screen placement, promote proper posture and lessen back strain.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise fortifies spine-supporting muscles, boosts circulation, and helps maintain a healthy weight. Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, and yoga are advantageous, adaptable to individual fitness levels.
- Stress Management: Persistent stress leads to muscle tension and resulting back pain. Integrating stress management techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and mindfulness into daily routines alleviates tension and fosters spinal health.
Knowledge of lifestyle’s effect on back health directs us towards positive changes for a healthier, pain-free back.
Diagnosis Procedures for Back Pain
Diagnosis of back pain involves medical history review, physical examination, and potentially, diagnostic imaging. Medical history provides information about the pain’s onset, duration, severity, and nature, along with potential contributing factors. The physical examination evaluates patient’s posture, spinal mobility, muscle strength, and nerve function to identify mechanical or neurological causes. In persistent cases or when a serious condition is suspected, diagnostic imaging such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs may be utilized. Pain perception understanding is critical as it influences the psychological impact and treatment response. This highlights the importance of a comprehensive diagnosis for effective back pain management.
Non-Invasive Treatments Available
Non-invasive treatments for lower back pain encompass physical therapy, pain relief medications, and acupuncture. Physical therapy strengthens spine-supporting muscles through targeted exercises. Pain relief medications alleviate discomfort and reduce inflammation. Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine practice, effectively manages chronic lower back pain, providing a holistic treatment approach. Each method offers relief without the need for surgical intervention.
Exploring Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a non-invasive treatment option for lower back pain. It aims to minimize pain and enhance mobility through Therapeutic Exercises and Pain Management Techniques, instead of medication or surgery.
- Therapeutic Exercises: These exercises enhance mobility, build muscle strength, and correct posture to alleviate lower back pressure. They encompass range of motion, strengthening, and flexibility exercises.
- Pain Management Techniques: Techniques such as heat/cold therapy, massage, and electrotherapy help manage pain by reducing inflammation and muscle tension.
- Patient Education: Physical therapists furnish knowledge on body mechanics and ergonomics to prevent recurrence of back pain.
Medication for Relief
Medications, such as painkillers, provide symptomatic relief for lower back pain, enhancing patients’ quality of life. However, there’s a risk of dependency, leading to potential adverse effects, requiring cautious monitoring. Natural supplements like Turmeric and Willow Bark, known for their anti-inflammatory properties, have gained popularity as alternative medicines. Despite their increasing use, their effectiveness varies among individuals and they should ideally complement mainstream treatments. These approaches, while non-invasive, require careful consideration and individualized management strategies for optimal results.
Benefits of Acupuncture
Acupuncture, originating from traditional Chinese medicine, is a non-invasive method recognized for its potential in managing lower back pain. Despite myths, research validates its efficacy, particularly when administered correctly by trained professionals.
- Traditional acupuncture versus electroacupuncture: Traditional technique involves needle insertion at specific body points to balance ‘Qi’ or energy flow. Electroacupuncture, the modern version, employs a minor electrical current between needle pairs, amplifying the therapeutic effect.
- Pain alleviation: Acupuncture triggers the nervous system, discharging neurochemical messenger molecules, altering pain perception.
- Drug-free alternative: Acupuncture presents a non-pharmacological option, devoid of dependence risk or severe side effects common with pain medications. It can complement chronic lower back pain management effectively.
Surgical Options for Severe Cases
For severe lower back pain, surgical options such as laminectomy, discectomy, fusion procedures, or disc replacement may be considered. Each surgery addresses specific conditions and has its own potential benefits and risks, including infection, hemorrhage, nerve damage, or even non-relief of pain.
Determining the nature of the patient’s pain is crucial for selecting the suitable surgery. For example, laminectomy, removing part of the vertebral bone to ease spinal nerve pressure, is ideal for lumbar spinal stenosis patients, while discectomy is suitable for herniated disc sufferers.
Post-surgery rehabilitation, including pain management, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications, is vital for recovery. The recovery time varies based on the specific surgery and the patient’s overall health.
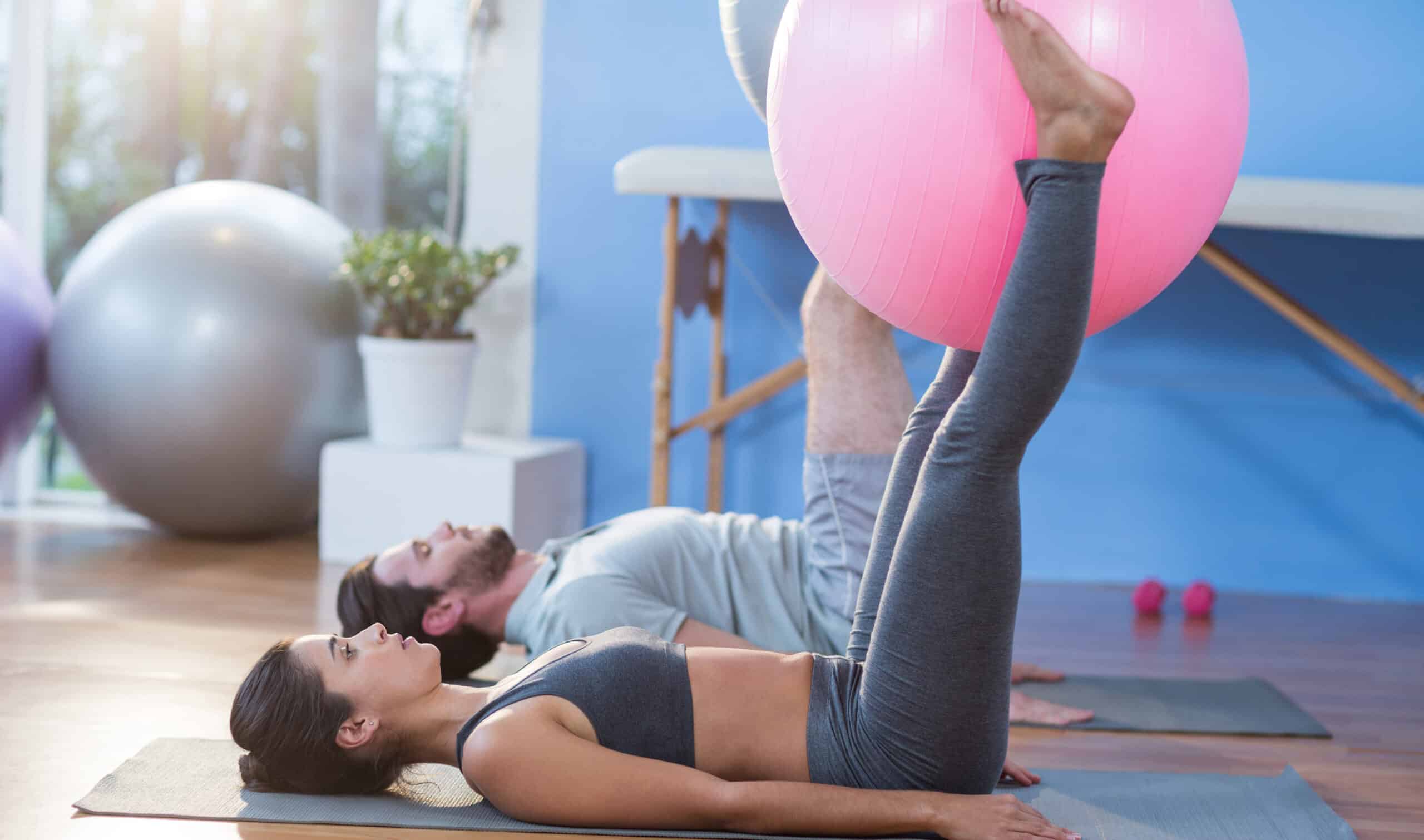

Importance of Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is crucial in managing and recovering from lower back pain. It provides a comprehensive, effective method for pain reduction and functional enhancement. Not only does it alleviate symptoms, but it also addresses the underlying cause of the discomfort, leading to long-term health improvements.
In the context of lower back pain, the primary objectives of physical therapy include:
- Posture correction: Physical therapists instruct patients on proper postural alignment to reduce lower back strain and prevent further injuries, as poor posture is a significant contributor to lower back pain.
- Strength and flexibility exercises: A series of movements are implemented to boost strength and flexibility, improving overall functionality and lessening pain in the lower back.
- Pelvic exercises: Specific exercises aimed at strengthening the pelvic muscles are utilized, offering substantial support to the lower back, minimizing pain, and increasing mobility.
These benefits highlight that physical therapy provides a comprehensive approach to managing lower back pain. It enables individuals to actively engage in their recovery, fostering a sense of control and positively influencing their quality of life.
Preventive Measures to Consider
Ergonomic furniture investment supports spine curvature, reducing lower back strain, beneficial for those with extended sitting or standing periods. Stress management, such as mindfulness, yoga, and deep breathing exercises, alleviates muscle tension, decreasing lower back pain risk. Regular physical activity strengthens back muscles, reducing injury susceptibility, but proper exercise form is crucial. Maintaining optimal body weight lessens back pressure, thereby decreasing pain likelihood.
Role of Diet in Back Pain Management
Diet’s role in managing back pain is significant. It aids in reducing inflammation, enhancing tissue health, and controlling body weight, thereby promoting spinal health.
- Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Consuming a diet with fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains helps lower inflammation, a key back pain factor. Foods such as berries, fatty fish, broccoli, avocados, green tea, and peppers have high anti-inflammatory effects.
- Dietary Supplements: Supplements like Omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, calcium, and magnesium can also enhance spinal health. They support bone health and control inflammation. Consultation with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regime is imperative.
- Hydration: Maintaining adequate hydration is crucial for spinal disc elasticity and fluidity, which promotes spinal health.
Coping Strategies for Chronic Sufferers
Managing chronic lower back pain involves fostering emotional resilience and understanding pain psychology. Emotional resilience, the ability to withstand and recover from stress, can be cultivated through methods like cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness-based stress reduction. These techniques aim to shift focus from pain to a balanced life perspective. Pain psychology, a subset of health psychology, explores the connection between psychological factors and pain perception. It reveals how beliefs, attitudes, and emotions can alter pain experience. Leveraging this understanding, sufferers can utilize strategies such as cognitive restructuring to transform negative pain-related thoughts into positive or realistic ones.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Some Genetic Factors That Can Contribute to Lower Back Pain?
Inherited spinal deformities, such as scoliosis and spina bifida, increase susceptibility to chronic lower back pain due to irregular spinal structure.
Does Weather Influence Lower Back Pain Symptoms?
Weather influences lower back pain. Cold, damp conditions exacerbate pain, necessitating effective pain management strategies. Understanding climate’s impact optimizes coping strategies development.
How Does Lower Back Pain Affect Mental Health?
Chronic lower back pain directly influences mental health by causing stress and lowering emotional resilience. It necessitates efficient stress management for maintaining mental health, emphasizing the link between physical and psychological health.
Are There Any Specific Yoga Poses to Help With Lower Back Pain?
Yoga poses, performed accurately with essential yoga equipment, offer lower back pain relief. Health professionals often advise Child’s Pose, Pigeon Pose, and Cat-Cow Pose.
Can Pregnancy Exacerbate Pre-Existing Lower Back Pain?
Indeed, pregnancy can amplify pre-existing lower back pain due to increased body weight and posture changes. Adopting suitable exercises and pain management strategies, supervised by professionals, can effectively control these intensified symptoms.